The relationship between job embeddedness and voluntary turnover intentions in the context of some situational factors - an analytical study of the opinions of faculty members at the College of Administration and Economics - Al-Qadisiyah University
Keywords:
Job embeddedness, ,job turnover, situational factorsAbstract
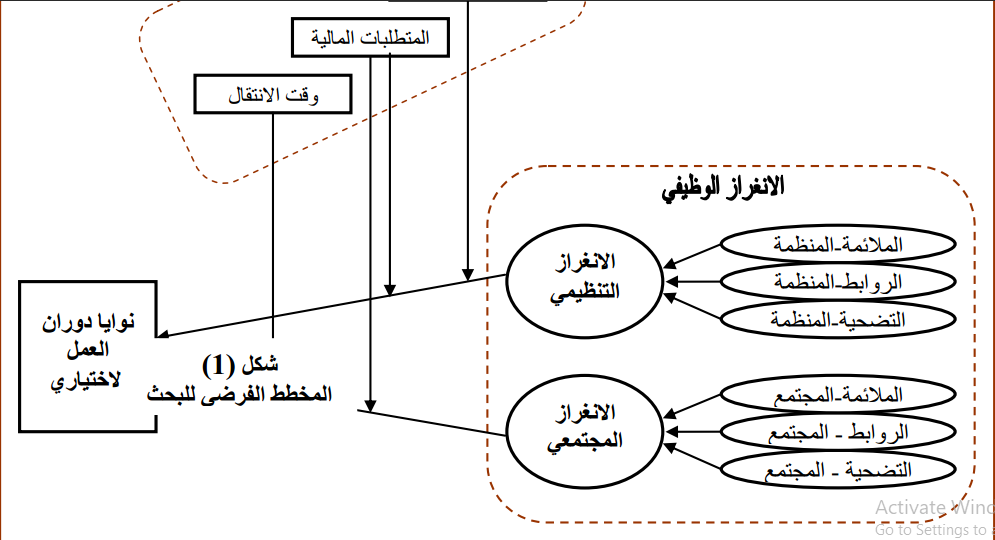
This research hypothizes that relationship between job embeddedness and voluntry turnover intensions is conditional relationship by existing number of situational factors: Work related nagitive shocks, commute time and financial requirements. Specifically, this research supposes that nagitive shocks and financial requirements influence relationship between organizational embeddedness and turnover intensions, and commute time and financial requirements influence relationship between community embeddedness and turnover intensions. The data were colleted by using questionnaire in a sample of (77) of faculty in College of Administrative and Economic- of AL-Qadisiya University. For testing the hypotheses and achiveing the research\'s goals, set of statistical tools such as Cronbach alpha, simple correlation coefficient and hierarchical multiple regression analysis were used. Results indicate that job embeddedness negatively related with turnover intensions. In addition to, the results indicate that situational factors (nagitive shocks, commute time and financial requirements) have role in influencing relationship between job embeddedness and turnover intensions. In lights of these results, set of conclusions and recommendation were formulated. One of these recommendations was reducing exposure to negative shocks by building \" Employee Voice System\".
References
References
Brett, J. F., Cron, W. L., & Slocum, J. W., Jr. (1995). Economic dependency
on work: A moderator of the relationship between organizational commitment
and performance. Academy of Management Journal, 38, 261–271.
Burton, J., Holtom, B., Sablynski, C., Mitchell, T. & Lee, T. (2010). The
buffering effects of job embeddedness on negative shocks. Journal of
Vocational Behavior 76, 42–51.
Cho, D. & Son, J. (2012). Job Embeddedness and Turnover Intentions: An
Empirical Investigation of Construction IT Industries. International Journal
of Advanced Science and Technology Vol. 40, 101-110
Cohen, A. & Golan, R. (2007). Predicting absenteeism and turnover intentions
by past absenteeism and work attitudes An empirical examination of female
employees in long term nursing care facilities. Career Development
International, Vol. 12 No. 5, pp. 416-432
Crossley, C. D., Bennett, R. J., Jex, S. M., & Burnfield, J. L. (2007).
Development of a global measure of job embeddedness and integration into a
traditional model of voluntary turnover. The Journal of Applied Psychology,
, 1031–1042.
Cunningham, G. & Fink, J. & Sagas, M. (2005). Extensions and Further
Examination of the Job Embeddedness Construct. Journal of Sport
Management, 19, 319-335
Deding, M., Filges, T., & Van Ommeren, J. (2009). Spatial mobility and
commuting: The case of two-earner households. Journal of Regional Science,
, 113–147.
Doran, L. I., Stone, V. K., Brief, A. P., & Ceorge, J. M. 1991. Behavioral
intentions as predictors of job attitudes: The role of economic choice. Journal
of Applied Psychology, 76: 40-46.
Felps, W., Hekman, R. D., Mitchell, R. T., Lee, W. T., Harman, S. W., &
Holtom, C. B. (2009). Turnover contagion: How coworkers' job embeddedness
and coworkers' job search behaviors influence quitting. Academy of
Management Journal, 52, 545–561.10. Frazier, P. A., Tix, A. P. & Barron, K. E. (2004). Testing moderator and
mediator effects in counseling psychology research. Journal of Counseling
Psychology, 51, 115-134.
Fryxell, G., & Wang, J. (1994). „The Fortune corporate „reputation‟
index, Reputation for what?‟, Journal of Management, 20(1), 1–14.
George, J. M., & Brief, A. P. 1990. The economic instrumentality of work:
An examination of the moderating effects of financial requirements and sex on
the pay-life satisfaction relationship. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 37: 357-
Griffeth, R. W., Hom, P. W., & Gaertner, S. (2000). A meta-analysis of
antecedents and correlates of employee turnover: Update, moderator tests, and
research implications for the next millennium. Journal of Management, 26,
–488.
Hair, J., Anderson, R., Tatham, R. & Black, W. (1998) Multivariale Data
Analysis, 5h Edition, Pearson Education Inc., India.
Hassell, C. (2005). An extension of the theory of job embeddedness: an
investigation of effect on intent to turnover of united states air force members.
Unpublished Dissertation, Air University, Air Force Institute of Technology.
Holtom, B. C., & Inderrieden, E. J. (2006). Integrating the unfolding
model and job embeddedness model to better understand voluntary turnover.
Journal of Managerial Issues, 18, 435−452.
Holtom, B. C., Mitchell, T. R., Lee, T. W., & Eberly, M. (2008). Turnover
and retention research: A glance at the past, a closer review of the present, and
a venture into the future. Academy of Management Annals, 2, 231–274.
Holtom, B., Mitchell, T., Lee, T., (2006). Increasing human and social
capital by applying job embeddedness theory. Organizational Dynamics, Vol.
, No. 4, pp. 316–331
Hom, P. W., & Griffeth, R. W. (1995). Employee turnover. Cincinnati,
OH: South-Western Press.
Kristof, A. L.: 1996, "Person-Organization Fit: An Integrative Review of
its Conceptualizations, Measurement, and Implications!, Personnel Psychology
, 1–49.
Law, K. & Wong, C. (1999). Multidimensional constructs in structural
equation modeling analysis; an illustration using the job perception and job
satisfaction constructs. Journal of Management, Vol. 25, No. 2., 143-160.
Lee, T. W., & Mitchell, T. R. (1994). An alternative approach: The
unfolding model of voluntary employee turnover. Academy of Management
Review, 19, 51–89.
Lee, T. W., Mitchell, T. R., Sablynski, C. J., Burton, J. P., & Holtom, B.
C. (2004). The effects of job embeddedness on organizational citizenship, job
performance, volitional absences, and voluntary turnover. Academy of
Management Journal, 47, 711–722.
Lee, T.W., Mitchell, T. R., & Sablynski, C. J. (1999). Qualitative research
in organizational and vocational psychology, 1979–1999. Journal of Vocational
Behavior, 55, 161–187.
Lev, s. & Koslowsky, M. (2012). Teacher Gender as a Moderator of the
On-the-Job Embeddedness–OCB Relationship. Journal of Applied Social
Psychology, 42, 1, pp. 81–99.
Levinson D, Kumar A (1994) Operational evidence for changing travel
patterns. ITE Journal, April 1994, pp 36–4027. Levinson, D. (1997). Job and housing tenure and the journey to work.
Ann Reg Sci, 31:451–471.
Maertz, C. P., & Campion, M. A. (1998). 25 years of voluntary turnover
research: A review and critique. In C. L. Cooper, & I. T. Robertson (Eds.),
International review of industrial and organizational psychology, Vol. 13. (pp.
–83)Chichester, England: Wiley & Sons.
Mallol, C. M., Holtom, B. C., & Lee, T. W. (2007). Job embeddedness in a
culturally diverse environment. Journal of Business and Psychology, 22, 35–44.
Martin, A. & Roodt, G. (2008). Perceptions of organisational
commitment, job satisfaction and turnover intentions in a post-merger South
African tertiary institution. SA Journal of Industrial Psychology, Vol. 34 No. 1
pp. 23 – 31
Martin, A. (2007). Employee perceptions of organizational commitment,
job satisfaction and turnover intentions in a post-merger institution.
Unpublished Dissertation, University of Johannesburg.
Mitchell, T. & Lee, T. (2001). The unfolding model of voluntary turnover
and job embeddedness: foundations for a comprehensive theory of attachment.
Research in Organizational Behavior, Volume 23, pages 189-246.
Mitchell, T. R., Holtom, B. C., Lee, T. (2001b). How to keep your best
employees: Developing an effective retention policy. Academy of Management
Executive, 2001, Vol. 15, No.4, 96-108.
Mitchell, T. R., Holtom, B. C., Lee, T. W., Sablynski, C. J., & Erez, M.
(2001a). Why people stay: Using job embeddedness to predict voluntary
turnover. Academy of Management Journal, 44, 1102–1121.
Mobley, W. H. 1977. Intermediate linkages in the relationship between
job satisfaction and employee turnover. Journal of Applied Psychology, 62:
-240.
Morrell, K. Loan-Clarke J., & Wilkinson, A. (2004). The role of shocks in
employee turnover, British Journal of Management, 15, 335–349.
Ng, T. & Feldman, D. (2010). The impact of job embeddedness on
innovation-related behaviors. Human Resource Management, November–
December 2010, Vol. 49, No. 6, Pp. 1067 – 1087
Nunnaly, J.C. & Bernstein, I.H. (1994). Psychometric theory. New York:
McGraw-Hill.
Oishi, S., Diener, E., Choi, D. W., Kim-Prieto, C., & Choi, I. (2007). The
dynamics of daily events and well-being across cultures: When less is more.
Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 93, 685–698.
Oyler, J. (2007). Core self-evaluations and job satisfaction: the role of
organizational and community embeddedness. Unpublished Dissertation,
Faculty of Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University.
Price, J.l. (2001). Reflections on the determinants of voluntary turnover.
International Journal of Manpower, 22(7), 660-624.
Reitz, O. & Anderson, M. (2011). An overview of job embeddedness.
Journal of Professional Nursing, Vol 27, No. 5: pp 320–327
Roodt, G. (2004). Turnover intentions. Unpublished document: University
of Johannesburg.
Rosenberg, Corcoran, S., Kovner, C. and Brewer, C. (2011). Commuting
to Work: RN Travel Time to Employment in Rural and Urban Areas. Policy,
Politics, & Nursing Practice 12(1) 46–5445. Sager, J.K., Griffeth, R.W. & Hom, P.W. (1998). A comparison of
structural models representing turnover cognitions. Journal of Vocational
Behaviour, 53(2), 254–273.
Samad, S. (2006). The Contribution of Demographic variables: Job
Characteristics and Job Satisfaction on Turnover Intentions. The Journal of
Human Resource and Adult Learning, 12-19
Saungweme, R. and Gwandure, C. (2011). Organizational Climate and
Intent to Leave among Recruitment Consultants in Johannesburg, South
Africa. J Hum Ecol, 34(3): 145-153.
Sekiguchi, T., Burton, J. & Sablynski., C. (2008). The role of job
embeddedness on employee performance: the interactive effects with leader–
member exchange and organization-based self-esteem. Personnel Psychology,
, 761–792
Smart, J. (1990). A Causal model of faculty turnover intentions. Research
in Higher Education, VoL 31, No. 5, 405-424.
Tanova, C. & Holtom, B. (2008). Using job embeddedness factors to
explain voluntary turnover in four European countries. The International
Journal of Human Resource Management, Vol. 19, No. 9, 1553–1568
Tett, R.P. & Meyer, J.P. (1993). Job satisfaction, organizational
commitment, turnover intentions, and turnover: Path analyses based on meta-
analytic findings. Personnel Psychology, 46, 259–293.
Tharenou, P., Donohue, R. & Cooper, B. (2007). Management Research
Methods. Published in the United States of America by Cambridge University
Press, New York
Zax, J. S., & Kain, J. F. (1991). Commutes, quits, and moves. Journal of
Urban Economics, 29, 153–165.
Zhang, M., Fried, D., & Griffeth, R. (2012). A review of job
embeddedness: Conceptual, measurement issues, and directions for future
research. Human Resource Management Review 22, 220–231.
Ramesh, A., & Gelfand, M. J. (2010). Will they stay or will they go? The
role of job embeddedness in predicting turnover in individualistic and
collectivistic cultures. The Journal of Applied Psychology, 20, 807–823.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2013 Economics and Administration College - Karbala University

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of their papers without restrictions.









