The Role of Talent Recruitment in promoting Proactive Work Behavior
An Exploratory Study of the Opinions of a Sample of Faculty Members in Some Private Universities and Colleges in the Holy Karbala Governorate
Keywords:
Talent recruitment, Proactive work behavior, Private universities in the Holy Karbala Governorate.Abstract
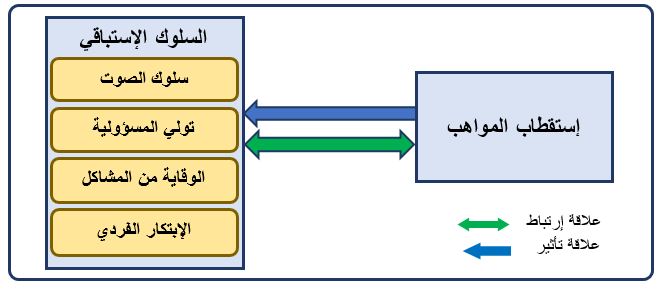
The main objective of this research is to test the effect of talent recruitment in promoting proactive work behavior, by surveying the opinions of a number of teaching staff in private universities - the holy governorate of Karbala. Distributed the questionnaire to (200) teachers. After sorting and checking the questionnaires, the number of valid questionnaires for statistical analysis reached (102 questionnaires. Statistical analysis of the data collected from the respondents was carried out using (SPSS v.25) and (AMOS) programs. The research reached some conclusions, the most important of which was that through the results of the statistical analysis of the research data; it was found that there is a positive and significant effect of talent recruitment in promoting proactive work behavior in the universities of the research sample. Some proposals, the most important of which is that if the private universities in the holy governorate of Karbala under discussion want to promote the proactive work behavior of their teaching staff, they should adopt the concept of talent recruitment.
References
Ali, F. M. (2021). Impact of proactive behavior on sustainable performance. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT), 12(12), 4416-4423.
Chan, J. Y., Chai, W. X., Koh, C. K., Ngo, S. L., &Teh, L. L. (2020). The impact of talent attraction, talent development and talent retention on job satisfaction in hospitality industry (Doctoral dissertation, UTAR).
Chia, H. W., & Sharon, K. P. (2013). Thinking and acting in anticipation: A review of research on proactive behavior. Advances in Psychological Science, 21(4), 679.
Dhurandhar, N., & Dai, B. (2021). Technology-driven practical efficiency in talent recruitment process in New Zealand. Journal of Applied Research & Practice: Issue 1.
Fuller, B., Marler, L. E., Hester, K., &Otondo, R. F. (2015). Leader reactions to follower proactive behavior: Giving credit when credit is due. Human Relations, 68(6), 879-898.
Grant, A. M., Parker, S., & Collins, C. (2009). Getting credit for proactive behavior: Supervisor reactions depend on what you value and how you feel. Personnel Psychology, 62(1), 31-55.
Hu, Y., Wu, X., Zong, Z., Xiao, Y., Maguire, P., Qu, F., ...& Wang, D. (2018). Authentic leadership and proactive behavior: the role of psychological capital and compassion at work. Frontiers in psychology, 9, 2470.
Idzna, A., Raharjo, K., &Afrianty, T. W. (2021, September). The Influence of Perceived Organizational Support and Proactive Personality on Organizational Commitment and Organizational Citizenship Behavior Among Banking Employees in Malang. In 3rd Annual International Conference on Public and Business Administration (AICoBPA 2020) (pp. 97-101). Atlantis Press.
Likhitha, K., & Pasha, D. M. (2019). A Study on Talent Acquisition Practices at DXchange. International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology, 7, 510-514.
Newburry, W., Gardberg, N. A., & Sanchez, J. I. (2014). Employer attractiveness in Latin America: The association among foreignness, internationalization and talent recruitment. Journal of International Management, 20(3), 327-344.
Nguyen, K., Nguyen, P., Do, T., Trinh, A., & Truong, V. (2020). Proactive personality, value congruence, perceived organizational support, and problem prevention behavior: A reciprocal moderated mediation model. Management Science Letters, 10(16), 4045-4054.
Onyando, A. (2018). Talent Management and Employee Retention Among Program Staff of Governance Civil Society Organizations in Nairobi, Kenya (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi).
Parker, S. K., Wang, Y., & Liao, J. (2019). When is proactivity wise? A review of factors that influence the individual outcomes of proactive behavior. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 6, 221-248.
Pasmore, W. A., Zlupko, G., Ajaikumar, N., Garcia, M., & Sinha-Chowdhury, S. (2021). Responsibility-taking Behavior: Validation of a Measure. In Academy of Management Proceedings (Vol. 2021, No. 1, p. 13836). Briarcliff Manor, NY 10510: Academy of Management.
Pawar, A. (2020). Prognostic Model for Employer Brand, Talent Attraction, and Employee Retention through Employee Value Proposition. Journal of Applied Management and Investments, 9(3), 133-152.
Rakthin, S., Punnakitikashem, P., Otakanon, B., &Oo, N. C. K. K. (2022). A Conceptual Framework about Employees’ Proactive Behavior and Supervisor’s Favorable Evaluation: Moderating Effects of Dissimilarity in Supervisors’ Cultural Dimensions. Archives of Business Research, 10(3).
Robinet, L. M. (2019). Reconceptualizing city branding to account for talent attraction: Cities as a place to work and live.
Sart, G., &Sezgin, H. F. (2022). The effect of university students' attitudes towards information and communication technologies on their tendency towards innovation. In EDULEARN22 Proceedings (pp. 8248-8255). IATED.
Syafitri, R., Ahadiat, A., &Hayati, K. (2021). The Effect of Strategic Leadership On Employees Creativity By The Mediation of Voice Behavior. SSRG International Journal of Economics and Management Studies, 8(1), 91-97.
Yao, K., Zhang, J., Qin, C., Wang, P., Zhu, H., &Xiong, H. (2022, May). Knowledge Enhanced Person-Job Fit for Talent Recruitment. In 2022 IEEE 38th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE) (pp. 3467-3480). IEEE.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 تبارك غائب ناصر المسعودي ، عبد الفتاح جاسم زعلان

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors retain the copyright of their papers without restrictions.



